FMP
How to Pull Clean Company Profiles Using a Free API
Feb 09, 2026
Accurate financial work starts with correct company identification. If a ticker is mismapped, a currency is assumed incorrectly, or a sector label is outdated, those errors quietly propagate through every downstream dataset.
Manual lookups do not scale and introduce avoidable risk. A free API that delivers standardized company profiles solves this at the source by creating a consistent “golden record” for each asset. This guide shows how to establish that baseline before integrating deeper financial data.
Getting Started: Obtaining Your Free API Key
Before you can pull leadership data programmatically, you need to establish a connection. This requires an API key, which acts as your unique digital ID for making requests.
Getting set up is straightforward and uses the documentation page directly:
- Navigate to the Financial Modeling Prep documentation page.
- Scroll down to the sign-up box and insert your email to start the registration process.
- Verify your email to create your account and generate your unique API key.
- Once verified, you can view your key and usage details on your dashboard.
This key allows you to make immediate calls to the API. For a more detailed walkthrough on setting up your environment, you can refer to this guide on how to sign up and use a free stock market data API.
Establishing a Reliable "Golden Record"
The immediate value of the Company Profile API is standardization. When you request data for a specific ticker, you aren't just getting a name; you are getting the distinct identifiers that allow you to map that company across other datasets like SEC filings or alternative data.
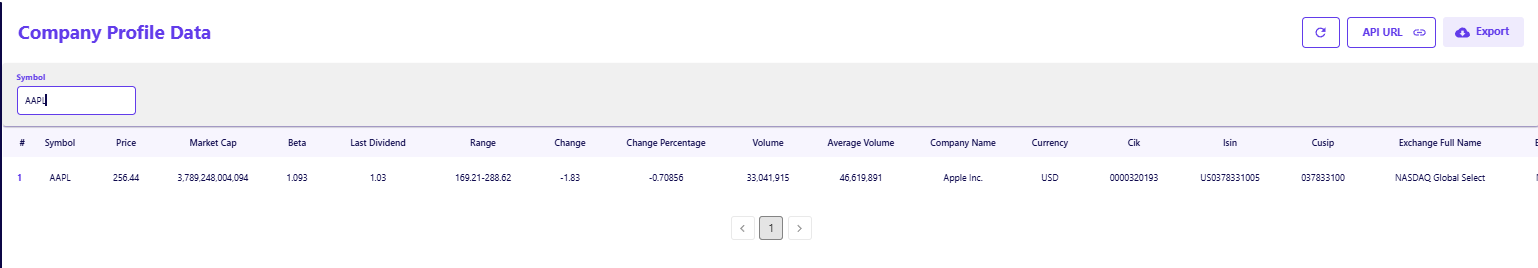
When you call the endpoint for a company like Apple (AAPL), the response returns a clean set of identification fields that eliminate ambiguity.
- Universal Identifiers: The API provides the CIK (0000320193), ISIN (US0378331005), and CUSIP numbers. These are critical for cross-referencing data with regulatory databases and ensuring you are tracking the correct security, even if a ticker symbol changes.
- Trading Context: You get immediate context on the stock's listing, including the Exchange (NASDAQ Global Select) and the Currency (USD). This prevents the common error of mixing currencies when analyzing multi-national peer groups.
- Market Scale: The response includes the current Market Cap ($3.78T) and Beta (1.093), allowing you to quickly filter out companies that don't fit your liquidity or volatility mandates.
If you are just setting up your environment, knowing what to do first after creating a Financial Modeling Prep account ensures you handle these initial requests correctly.
Validating Sector and Business Operations
Beyond the hard numbers, qualitative data is essential for screening and peer grouping. The API returns the descriptive metadata required to bucket companies correctly.
- Automated Descriptions: Instead of manually writing summaries, you can pull the Description field. For Apple, this provides a detailed paragraph explaining that they "design, manufacture, and market smartphones, personal computers, tablets, wearables, and accessories". This text is ready for automated reports or NLP analysis.
- Sector & Industry Tags: The Sector (Technology) and Industry (Consumer Electronics) fields allow you to systematically categorize stocks. If you are building a screener, these tags ensure you are comparing Apple to other hardware manufacturers rather than software services.
- Leadership Checks: The profile also lists the CEO (Timothy D. Cook) and Full Time Employees (164,000), providing a quick proxy for company size and current leadership stability.
Scaling from Lookup to Bulk Management
The true power of an API is revealed when you need to track more than one company. While the single-symbol endpoint is perfect for testing and validation, your workflow will eventually require bulk handling.
The Company Profile Bulk API allows you to retrieve this same level of detail for the entire market or specific indices. This is essential for maintaining a "master list" of active coverage. By running a daily or weekly script, you can catch changes—such as a company moving sectors, changing its name, or delisting—without manual audits.
As you expand your coverage, deciding which Financial Modeling Prep data you should start with helps you prioritize which endpoints to integrate next.
Data Hygiene as a Competitive Advantage
Automating the retrieval of company profiles is not about saving five minutes of copy-pasting; it is about eliminating the operational risk of bad data. By using a free API to standardize your inputs, you ensure that every subsequent calculation in your model is based on accurate, verified identity information.
This low-risk entry point allows you to validate the utility of the data structure immediately. Once you trust the metadata, you can confidently expand into more complex datasetslike financial statements or valuation metrics. For continued learning on structuring your environment, explore our five guides to building your market data foundation. Additionally, as you move toward backtesting, reviewing how to get historical market data and why it matters for model validation will help ensure your historical baselines are just as robust as your current profiles.
Automating the retrieval of company profiles is not about saving five minutes of copy-pasting; it is about eliminating the operational risk of bad data. By using a free API to standardize your inputs, you ensure that every subsequent calculation in your model is based on accurate, verified identity information.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I sign up for the free API?
To sign up, visit the documentation page, scroll down to the sign-up box, and insert your email address. No credit card is required.
Is the free plan really free forever?
Yes, the free plan is designed for personal use and allows for 250 requests per day. This gives you ample room to explore endpoints without an expiration date.
Do I need a credit card to get an API key?
No, the free tier is accessible without any payment information. You only need to provide a credit card if you decide to upgrade to a premium plan for higher rate limits or additional datasets.
Is the market cap in the profile real-time?
The Market Cap and Price fields in the company profile are typically updated dynamically during trading sessions, providing a snapshot of the company's current valuation.
What is the difference between Sector and Industry?
Sector is a broad classification (e.g., Technology), while Industry is a more specific sub-category (e.g., Consumer Electronics). Using both allows for more precise peer filtering.
Can I get the company logo via the API?
Yes, the profile data often includes a link to the company's logo, which is useful for building visual dashboards or branded reports.
Do I need a paid plan to access US company profiles?
No, the standard company profile data for US stocks is generally accessible via the free API tier, making it an excellent starting point for testing.
Why is the CIK number important?
The CIK (Central Index Key) is the unique identifier used by the SEC (0000320193 for Apple). Using the CIK ensures that if a company changes its ticker symbol, you can still link it correctly to its regulatory filings.
Does this API cover ETFs?
While the Company Profile endpoint focuses on operating companies, there are separate endpoints specifically designed to provide profile data and holdings for ETFs.
How do I handle companies with multiple share classes?
The API distinguishes between share classes via unique symbols (e.g., GOOG vs. GOOGL). You should query the specific ticker you are analyzing to get the correct price and volume data for that class.

Top 5 Defense Stocks to Watch during a Geopolitical Tension
In times of rising geopolitical tension or outright conflict, defense stocks often outperform the broader market as gove...

Circle-Coinbase Partnership in Focus as USDC Drives Revenue Surge
As Circle Internet (NYSE:CRCL) gains attention following its recent public listing, investors are increasingly scrutiniz...

LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton (OTC:LVMUY) Financial Performance Analysis
LVMH Moët Hennessy Louis Vuitton (OTC:LVMUY) is a global leader in luxury goods, offering high-quality products across f...

